Understanding RS-232C Cables
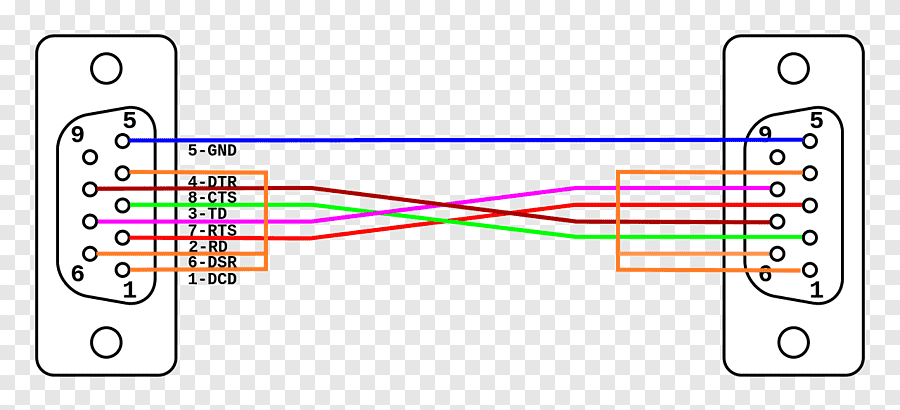
Looking at the category of hardware as well as communications, the RS-232C cable is an icon for data transmission. It has been a part of the progress of serial communication protocols that have been instituted. This article also seeks to give detailed information about RS-232C cables hence covering histories of such cables, their structures and characteristics, uses as well as problems that may prevail. We will also consider pts associated with the main topics and answer some questions Based on the above arguments, we will be able to draw Pt Six Key Points. What is an RS-232C Cable? The RS-232C is the Recommended Standard 232C used in serial communication and it outlines the electrical aspects and timing of signals, along with their meaning in serial communication. Arising from the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) in the early ’60s, RS-232C is employed commonly for the connection of computers with peripheral equipment like modems, printers, and a lot of other industrial appliances. Key Characteristics of RS-232C Signal Transmission: RS-232C utilizes serial data transfer, which means that data is transferred serially, one bit at a time, on a single line. Voltage Levels: It usually works with voltage ranges of +3 V to +15 V for a logical ‘0,’ and -3V to -15V for a logical ‘1.’ Connector Types: DB9 (9-pin) and DB25 (25-pin) connectors are the most frequently used, although there are several other types of them. Data Rate: It is capable of supporting data rates of up to 115200 bits per second, although most of the practical applications of the standard are likely to use much lower data rates. Historical Evolution of RS-232C RS-232C was the improvement of the initial serial communication standards, including RS-232, RS-232A, etc. The “C” refers to an improved version that has better features with regard to the dependability of transmitted data and compatibility. RS-232C gradually grew into a widely used standard for serial communication in many different electronics. Technical Specifications Connectors and Pinouts DB9 Connector: The other type of connector is the DB9, which is a 9-pin connector that is smaller as compared to the formerly mentioned type. DB25 Connector: However, the DB25 is a larger 25-pin connector often used in now outdated systems. Common Pin Functions Pin 1 (DB25) / Pin 1 (DB9): Facilities in EIA: Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Pin 2 (DB25) / Pin 2 (DB9): Receive Data (RD) Pin 3 (DB25) / Pin 3 (DB9): Transmit Data [TD] Pin 4 (DB25) / Pin 4 (DB9): Data terminal ready (DTR) Pin 5 (DB25) / Pin 5 (DB9): SG or Signal Ground Pin 6 (DB25) / Pin 6 (DB9): A paper called Data Set Ready (DSR) Pin 7 (DB25) / Pin 7 (DB9): Request to Send (RTS) Pin 8 (DB25) / Pin 8 (DB9): Clear to Send or CTS Pin 9 (DB25) / Pin 9 (DB9): Ring Indicator (RI) Signal Levels and Timing RS-232C signals are differential; that is, signals on RS-232C are in terms of voltage differences on the signal lines. The standard presents a minimal signal voltage of ±3V, with the maximum signal voltage that is allowed ranging from ±15V. Timing and its management are always important to ensure that there is actual delivery of the intended data properly with the understanding that timing is central to the mechanism of passing data where the sender and the receiver are always supposed to agree. Data Framing RS-232C encloses data with start bits, data bits, optional parity bits, and stop bits. A typical frame includes: Start Bit: Marks the start of a data frame, so it is “>=group.”. Data Bits: Typically, bits 7 and 8 and, at times, 7 and 9, hold the actual information. Parity Bit: It has this optional error-checking bit incorporated into its schemes. Stop Bits: One or more ‘0’/ ‘1’ bits to mark the end of the data frame. Applications of RS-232C Cables There are many applications for RS-232C cables because of their ease and reliability, inclusive of the following. 1. Computer Serial Ports Before the introduction of USB, RS-232C had been the standard interface for mice, modems, and serial printers to link with the computer. 2. Industrial Equipment Most industrial machines and equipment use RS-232C for the interconnection of the devices as well as the control systems. Lithography is preferred for its durability and ease of use in industries, especially in factories. 3. Networking Equipment Although nowadays RS 232 C is not very frequently used in modern networks, it is useful to configure network devices and manage network equipment through serial ports. 4. Medical Devices RS-232C is applied to some medical equipment for transmitting information and controlling the equipment. That is why it can be recommended for critical applications since it is very reliable and easy to implement. Troubleshooting Common Issues Still, when utilizing RS-232C connections, users can experience certain problems. Here are some common problems and solutions: Here are some common problems and solutions: 1. No Communication Issue: Despite the correctness of the connections, devices do not communicate. Solution: Check all cable connections and also ensure that both devices are configured with the right baud rate, parity, and data bits. 2. Data Corruption Issue: Sometimes, the data that is received is either distorted or doesn’t contain the right information. Solution: Verify if signal groundings are correct on all signals and avoid the use of cables that are too long. Disturbance and disruption also lead to data embellishment or alteration. 3. Connection Failures Issue: There is no connectivity between devices at all. Solution: Check the continuity of the connector, or also check if the RS-232C connectors have any damage or bent pins. Check that all control lines (for example, RTS and CTS) are properly connected and work correctly. FAQ 1. RS-232 is hardware, whereas RS-232C is a protocol. RS-232C is the enhanced version of the general series RS-232 standard. They encompass changes to the signal strength, timing, and general dependability. While the term “RS-232” is used to describe the wider range of standards, most people imply “RS-232C” and therefore use the
