The risk is left over after efforts have been made to identify and reduce some or all risk types is known as residual risk. One should consider residual risk for several reasons. The risk left over after procedure enhancements and security measures have been implemented is known as residual risk and it should be taken into account first.
What are residual hazards?
The necessity of including a residual hazards section in the health and safety manual has grown since 2007 CDM. This is especially confounding to some subcontractors since it looks a much like the risk assessment they have to do before they begin work in April 29, 2010
Which residual hazards are appropriate to mention in the O&M and Handover Health and Safety manuals?
Since 2007 CDM necessity of including a residual hazards section in the safety and health manual has grown. The fact that this seems to be quite similar to the risk assessment that they must complete before beginning work causes some subcontractors great confusion.
Different Residual Hazard Types
There are several different kinds of residual hazards that might still provide a danger after the design stage. Environmental risks are a typical form of risk that may not be completely eradicated by basic precautions, such as pollution or contamination.
Human error related risks are a different kind of danger when safety precautions are taken yet faults in operations or processes might still result in accidents.Another important class of residual hazards is mechanical risks which include things like defective equipment or malfunctioning machinerythat might cause harm if not adequately supervised.
Another issue is chemical risks which can expose people to dangerous materials even after precautions have been taken.Furthermore the health of employees might still be impacted by ergonomic risks associated with repeated jobs or poorly designed workstations.
Examples of Residual Hazards in Different Industries
Different sectors may have residual hazards, which provide dangers that were not previously taken into account during the design phase. Inadequate communication between contractors and subcontractors in the construction sector can result in safety lapses, such inappropriate equipment usage or unfinished scaffolding inspections.
In healthcare settings, patients may be at risk of pharmaceutical mistakes either from imprecise communication between staff members or from difficult-to-read handwritten prescriptions. The industrial sector is nevertheless vulnerable to risks arising from maintenance errors or human mistake that cause equipment to malfunction.
Moreover, there are still risks in the transportation industry from things like insufficient safety regulations or driver training programs. In each of these several businesses, it is crucial to identify and reduce lingering risks.
Architectural
| Residual Hazard | Location |
| Working at Height | Glass Panels in Facade |
| Glass Breakages | Bowl side Glazing |
| Falls from Height | Decorating Walls and Ceilings |
How do we classify hazards?
No matter where you work or what industry you’re in, workplace hazards can be divided into seven categories that can make them easier to mitigate and help you stay organized as you address them.
No matter what threats your team faces, they fall into one of the following categories. Here is how to identify and mitigate them.
What are the 7 most common workplace hazards?
The 7 most common workplace hazards are:
- Safety hazards
- Biological hazards
- Physical hazards
- Ergonomic hazards
- Chemical hazards
- Work organization hazards
- Environmental hazards
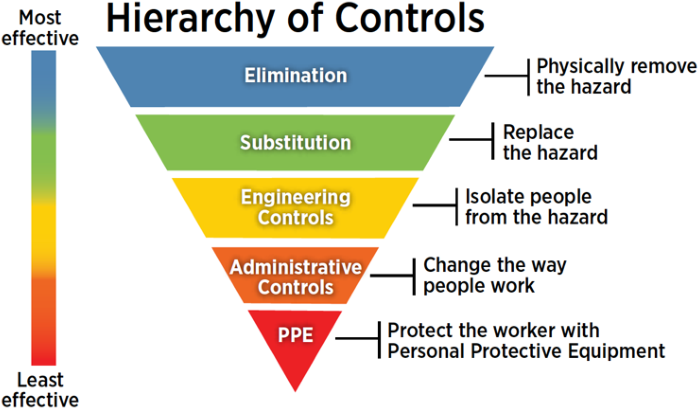
Residual risk
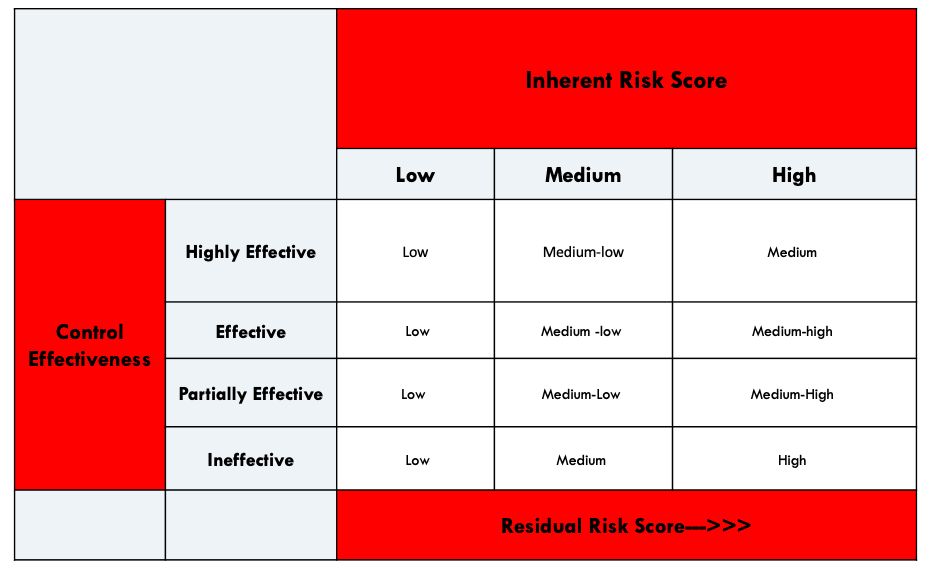
Residual risk is the level of risk, danger associated with an action, event after natural or inherent risk has reduced by risk management.
The general formula for calculating residual risk is:
Residual risk=(inherent risk)-(impact of risk controls)
Here, the general concept of risk is (Threat × Vulnerability), or (Severity × Probability).
An example of residual risk is the use of seat belts in cars. Wearing and using seat belts reduces the overall severity and chance of injury in a car accident. However there is still a chance of injury when using them H. Residual risk.
In an economic context residual means the amount remaining at the end of the process. It’s the remainder. In the property rights model shareholders bear the residual risks and therefore the residual benefits.
FAQS
What are examples of all hazards?
The term all hazards refers to both natural and man-made disasters and could be
- Natural disasters.
- Disaster and emergency threats.
- Cybersecurity incidents.
- Power outages and IT outages. Man-made hazards.
- Security-related issues.
- Fire on site.
What does the term hazard mean?
Definitions of hazards
A hazardous material, human behaviour, occurrence, or state is referred to as a hazard. It might result in death, serious injury or severe health effects, destruction of property, loss of services and livelihoods, disturbance of the social and economic order, or harm to the environment.
What are the different hazard classifications?
- GB CLP Hazard Pictograms
- Explosive (symbol: exploding bomb)
- Flammable (symbol: flame)
- Oxidizing (symbol: flame on circle)
- Corrosive (symbol: corrosion)
- Acutely toxic (symbol: skull and crossbones)
- Dangerous to the environment (symbol: environment)
- Dangerous to health/harmful to ozone (symbol: exclamation mark)
What are the three main hazards?
The Hazards are recognize as a part of a hazard analysis and rated according to their probability of occurrence and the severity they can lead to illness or injury. All hazards are evaluated and classified into three groups biological hazards, chemical hazards and physical hazards.
What are 10 examples of physical hazards?
Physical hazards include slips, trips, falls, electricity, noise, vibration, radiation, heat, cold and fire.
What are the most common hazards?
Being aware of hazards in your home is the first step to avoiding them. The most common household hazards include fire, poisoning and allergies. House fitting can also pose hazards such as falls, choking, cuts and burns.
What are some examples of hazards?
Health hazards include chemical hazards solvents, glues, paints, toxic dusts etc., physical hazards noise, radiation, heat etc., biological hazards infectious diseases ergonomic risk factors heavy lifting repetitive motions and vibration.
What is residual disaster risk?
Residual risk is disaster risk that persists despite effective disaster prevention measures and requires maintaining emergency response and recovery capabilities.