Within the dynamic realm of technological advancement, the utilities sector of today is concentrating its attention on business intelligence applications to maximize outputs and satisfy customers. By giving utilities the knowledge and resources needed to successfully interact with one another and adjust to shifts in energy production, distribution, and consumption, business intelligence helps utilities maintain a competitive edge.
The purpose of this paper is to identify the BI strategies that utilities are using to manage their business processes and improve customer service.
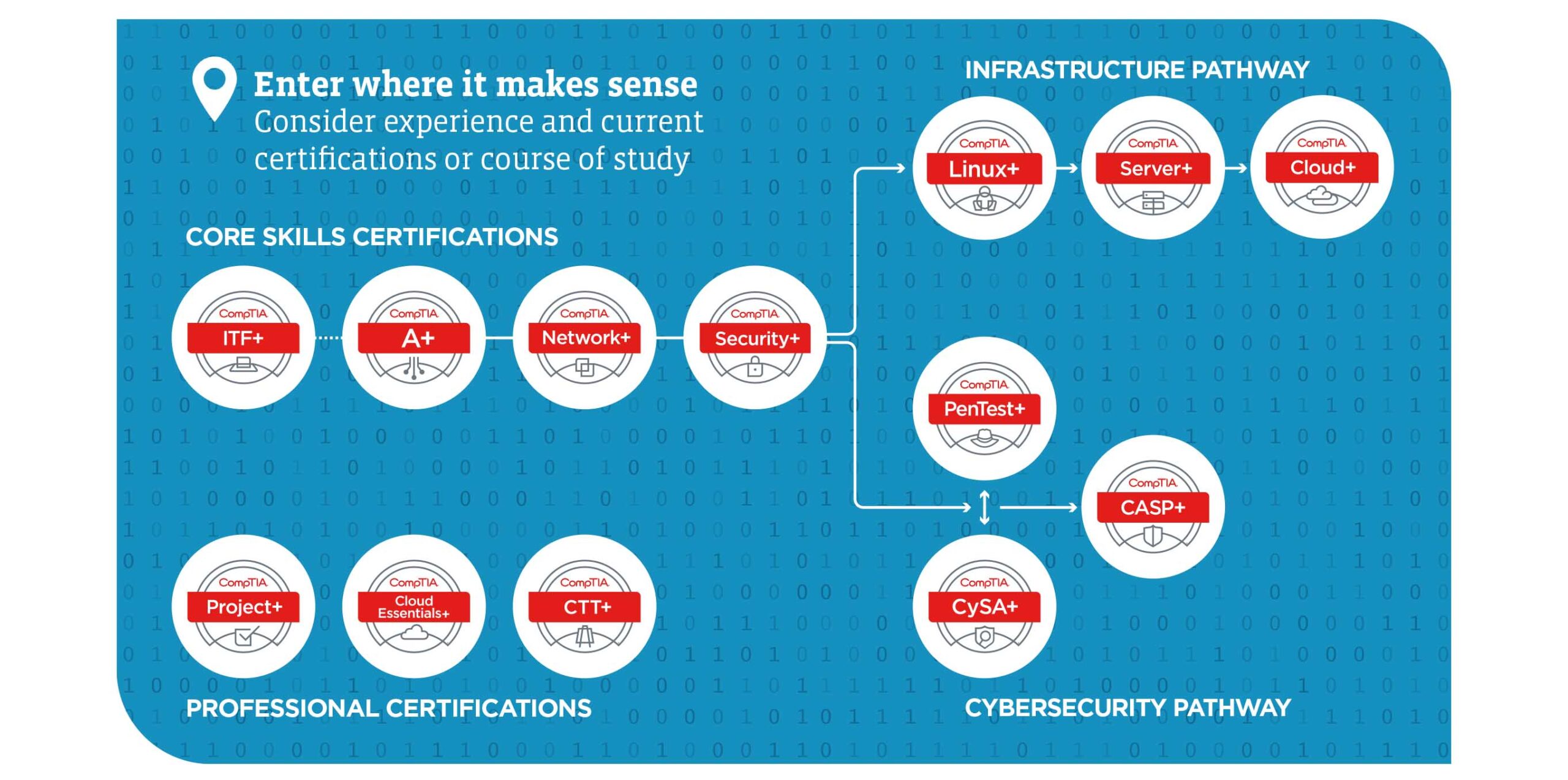
The Business Intelligence Function in Utilities
Applications and technology used in gathering, merging, analyzing, and presenting business data in an understandable format are all part of business intelligence (BI). Within the utility industry, business intelligence (BI) tools facilitate the transformation of data into a tool that has meaning for the organization, thereby enhancing decision-making procedures. Utility companies get their data from a variety of sources, including sensors, smart meters, and consumers.
These systems aid in the gathering and analysis of data to help identify intelligent patterns, trends, or areas that require improvement.
Improving the Effectiveness of Operations:
Increasing an organization’s operational effectiveness is the primary benefit of business intelligence for the utility industry. They must manage the production and distribution of utilities like water, natural gas, and electricity via a vast network of pipelines, power plants, and grids. Utilities can monitor the condition of these assets, determine when maintenance is due, and improve resource management with the use of such solutions.
For instance, data analysis can be used to anticipate broiler contamination before the indicators affect public health. This not only improves the credibility of the service but also reduces costs associated with breakdowns and/or repairs of the service, which are frequently highly expensive during emergencies.

Enhancing Client Contentment:
Customer satisfaction is a critical component of utility companies’ operations. When applied, business intelligence gives utilities a deeper comprehension of their consumers’ needs and expectations. Utilities can create more specialized services and rates based on customer contact information, billing patterns, and usage patterns.
BI tools, for example, can be used to identify customers who use a lot of energy and then present them with deals or helpful advice with an emphasis on energy conservation. Advanced analytics allows for the establishment of patterns that, for example, indicate periods of higher usage, thereby preserving a steady supply of services.
Enhancing power management and demand estimation:
For utilities to satisfy the demands of their customers, they must understand demand from the appropriate angle. With the help of Utilities Business Intelligence, utilities can now predict future consumption patterns based on historical data, weather patterns, and any market trends that may have been noticed.
This helps the utilities get the most out of their resources, balance their energy sources, and reduce costs wherever possible. Furthermore, since utilities can use BI tools to learn about consumption patterns and create adequate demand response programs to help customers save money or move their power usage to off-peak hours, they can aid in energy management.
Promoting Corporate Responsibility and Compliance:
The utilities sector is very regulated, and it has to meet very expected sustainability standards. To sum up, business intelligence can be regarded as the key to ensuring that utility companies meet the aforementioned obligations. As the integrated means for data reporting and analysis, BI systems help utilities measure their outcomes regarding regulations and sustainability goals. For instance, BI tools can detect the levels of emission rates, measure the use of renewable energy in industries, and confirm environmental policies. It not only assists the utilities in avoiding such fines but also adds to their image as being prudent, safer, and more sustainable organizations.
Utilizing the Utilities Sector Successfully:
Several utilities have already provided the ideal illustration of the benefits business intelligence can offer to the corporate sector. An example of a successfully deployed extensive Utilities Business Intelligence platform is the merging of data from business processes by the largest energy provider in the United States. People were able to watch the generation, distribution, and consumption of power in real-time thanks to this system, which increased generation reliability and efficiency. The company pledged to save millions of dollars in maintenance costs and stabilize the unplanned shutdown by 20% through the use of predictive analytical solutions.
A European water utility company that uses business intelligence to enhance leak detection is another excellent example. Through the analysis of sensor data and customer feedback, the utility was able to identify and address leaks early on, resulting in a 15% reduction in water waste and a higher customer satisfaction rate.
Difficulties and Considerations:
Notwithstanding these benefits, companies still have a lot of obstacles to overcome to successfully deploy Utilities Business Intelligence systems. Data aggregation from various databases and data sources is one of the main issues facing EMS. Data integration is difficult because utilities such as electric, gas, and water use systems that were designed as standalone units rather than as integrated systems.

Furthermore, this calls for addressing concerns with the quantity, quality, and accuracy of the data used in the analysis. Being able to locate and hire skilled personnel to staff and offer professional analysis of BI systems is another important consideration. T
o use cutting-edge analytics tools, it stressed how important it is for utilities to train and develop a skilled workforce. Nonetheless, cybersecurity is important because BI systems frequently handle sensitive data, making accessibility difficult. To guard against cyberattacks and data loss, utilities also need to assess their computer security posture.
FAQs
What is utility intelligence?
Utility Intelligence provides specialty consulting services often related to an operational technology project or programs envisaged or in flight.
What is a utility business?
Utilities are the market sector that includes companies that produce or deliver electricity, water, natural gas, and related services to the public. The companies within this sector operate under strict regulations because of the essential nature of the products and services they deliver.
What are the advantages of business utility?
They automate workflows and ensure smooth information flow between different departments, enhancing operational efficiency. Improved Data Accuracy: With integrated software applications, data is entered and updated in real-time across different modules.
Conclusion:
Utilities Business Intelligence (BI) applications are being used by the utilities industry to improve outputs and satisfy customers. Maintaining a competitive edge, BI assists utilities in adapting to shifts in energy consumption, distribution, and production. Data from sensors, smart meters, and customers is gathered, merged, analyzed, and presented as part of BI strategies.
They make it easier to make decisions, make operations work better, make customers happy, and predict how people will use things in the future. Data aggregation, integration, and cybersecurity remain challenges even though BI systems also promote compliance and corporate responsibility.